What Will Happen if OCD is Left Untreated?
Medically Reviewed By – Juliet Gustafson, LMSW

One of the most frequently asked questions in the OCD community is What Will Happen if OCD is Left untreated? Unfortunately, due to the stigma surrounding mental health illnesses people tend to delay the treatment process. This of course has detrimental effects both in the short and long term.
This post is all about What Will Happen if OCD is Left Untreated?
What Are the Dangers of OCD?
Obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) is ranked by the (The World Health Organization) as one of the most disabling mental health disorder for a reason. Having OCD is no joke and the impact it has on daily life is a heavy burden to carry.
It has many dangers and/or negative impacts on everyone who is diagnosed by the disease and/or family members observing their loved ones suffer immensely from it. From physical damage to tarnishing social relationships, obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) is a versatile disorder.
Some areas of daily life impacted by OCD include the following –
- Educational Endeavors (school & college)
- Career Growth
- Social Relationships
- Social Interactions
- Leisure Alone Time
- Regular Everyday Chores
- Quality of Life in General
- Physical illness
- panic attacks
- Repetitive behaviors
- Distressing thoughts
- Skin complications
- Losing control
- Experience anxiety
- Abnormal behavior
- Negative feelings
- Social isolation
Students will observe that their obsessive symptoms will skyrocket during these times, making it even harder to focus and study. These implications usually result in bad grades, low GPA scores and no less amount of anxiety and risk of developing co occurring disorders.
How Severe Can OCD Get?
Obsessive compulsive disorder is one of the top 10 most debilitating conditions worldwide according to the World Health Org (WHO). OCD can get pretty severe and significantly disabling as a mental health disorder. Severe obsessive compulsive disorder occurs when obsessions (and recurring thoughts) and compulsions increase in frequency and severity.
As symptoms worsen, OCD begins interfere with everyday life such as attending school/work. Obsessions begin to intensify while compulsions become more time consuming. This is can be due to abnormal stressful situations such as a death of a loved one for example.
Moreover, therapists usually use diagnostic tools such as the Y-BOCS OCD test. The Yale Brown Obsessive-Compulsive Scale is regarded as the “gold standard” in the measurement of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) symptoms severity and treatment response. According to the Y-BOCS curriculum, any score between (24 – 31) is considered severe OCD symptoms.
Related Article(s) – What Causes OCD To Get Worse?
What Are The Long-Term Effects of OCD?
Since OCD is a chronic disorder, symptoms (lifetime prevalence) will most likely occur for the rest of your life. This of course has many implications on both short and long term effects. However, there is hope here. According to a study conducted in 2013, 39% of participants experienced a partial (22.1%) or full (16.9%) remission within a 5 year period.
Moreover, an earlier study conducted between 1978 and 2008 found that a whopping 60% of individuals with OCD experienced symptom remission over a 30 year follow up. As we explained earlier, OCD symptoms may be reduced but rarely ever go away.
Other Long-Term Effects of OCD
- Social interactions become more challenging
- If not treated, OCD may lead to the onset of other comorbid diseases (depression, anxiety and eating disorders)
- If unaware, patients may start developing substance abuse (drugs and alcohol) to help ease anxiety and stress making the disease worse in the process
- the risk of developing OCD is greater for first-degree relatives of affected individuals (such as siblings or children)
How Does OCD Affect a Person’s Life?
Love Reading? Checkout our MUST READ OCD books List!
The Impact Of OCD On Social Relationships
This is a big one. Since OCD makes people attach meaning to their obsessions and unwanted thoughts, most patients tend to live within their thoughts (also called ruminations) instead of the real physical world.
This tends to impact social relationships in school, college and work (professional life) greatly. OCD sufferer(s) will begin to feel and act awkwardly in the presence of obsessions, which translates poorly in regards to social interactions and social acceptance.
Thus, people with OCD tend to stay away from social interactions/meetings and prefer to be left alone, slowly becoming introverts in the process.
Furthermore, people with OCD may find it very difficult to formulate friends and high quality relationships in school and/or work due to the nature of the disease (obsessive compulsive cycle). This is all due to untreated ocd.
The Impact Of OCD On Education
In this fast evolving world we live in, modern education is becoming more and more challenging. However, it’s extra hard when someone has Obsessive compulsive disorder. As we stated earlier, the meaning we give to our obsessions and intrusive thoughts, sensations, or urges are a main feature for the disease, thus OCD patients tend to live within their thoughts and feelings.
These obsessions and compulsions (repetitive behaviors) will take away most of your time and energy, leaving you with nothing more than heartache and suffering
Instead of having your mind and energy focus on quizzes, projects and tests, you find yourself living within your thoughts. Moreover, OCD symptoms are usually triggered in stressful times such as midterms and finals (in regards to education).
Students may observe that their obsessive symptoms will skyrocket during these times, making it even harder to focus and study. These implications can result result in bad grades, low GPA scores and no less amount of anxiety. This is a direct result of untreated ocd.
The Impact Of Physical Damage From OCD
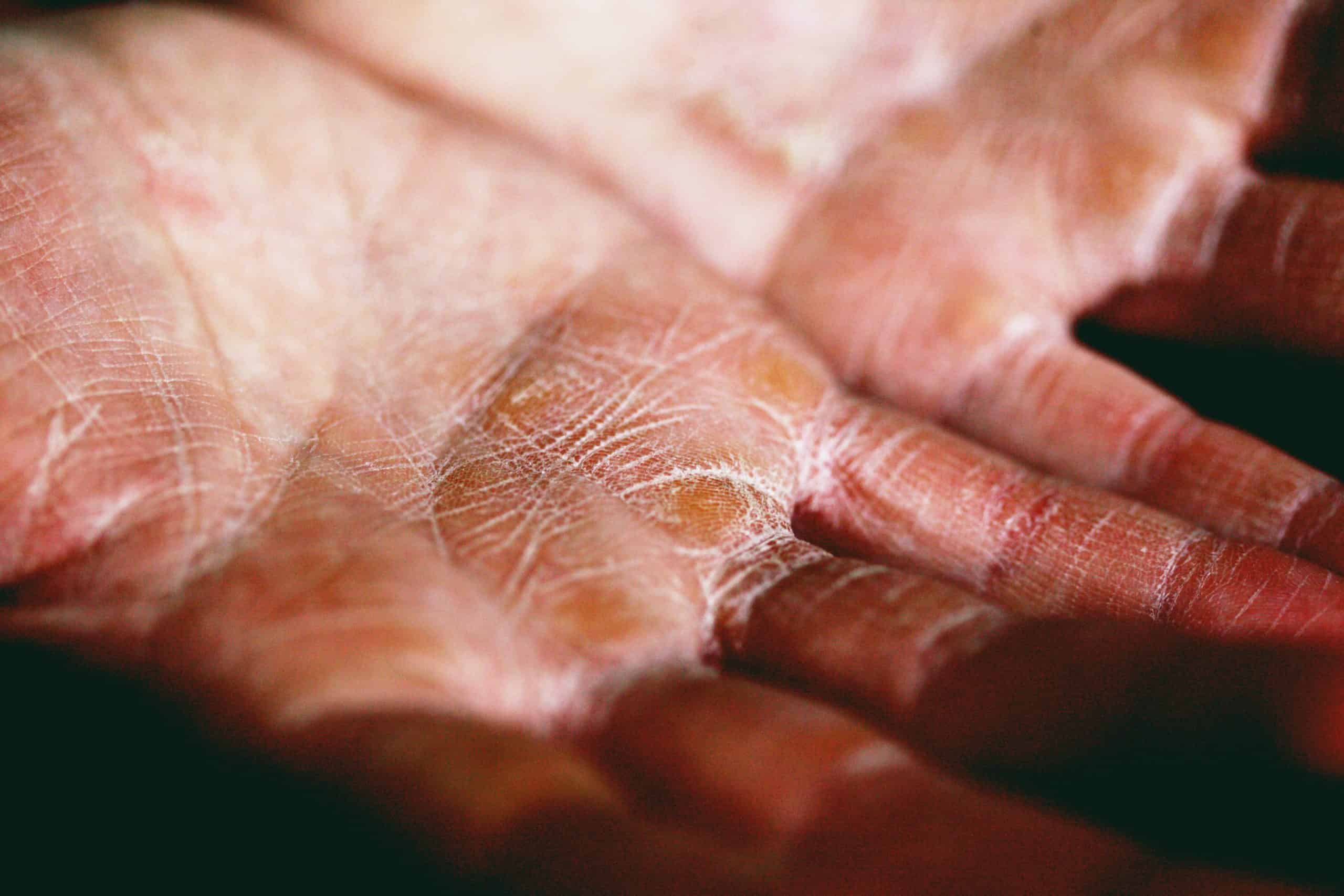
Not only does OCD affect a person mentally but it also has physical effects too. As we stated in earlier posts, there are many subtypes of OCD, and each have their own potential risks for physical harm.
For example, Contamination OCD is a common subtype of the disease in which patients experience obsessive thoughts regarding being “contaminated”.
The immediate response of such people would be to wash their hands excessively over and over again until it “feels right”. These compulsive actions usually result in red and raw bleeding skin, dry skin and blistering.
The Impact Of OCD On Entertainment
It is well established by now through research and patient’s feedback that OCD has a tendency to “stick” to the things we love. These aspects may include people, places and activities you enjoy doing. Your OCD will most likely revolve around things (people, places, activities) you care about. This is where people with OCD find it hard to enjoy things they used to love pre diagnosis.
For example, you are a cat person and love your cat dearly. Since you care about your cat, OCD obsessions will most likely revolve around your cat. You could have intrusive thoughts about harming your cat, being sexually active with your cat (unwanted sexual thoughts) and abusing/torturing your lovely pet.
These obsessions will make you doubt yourself, increase feelings of anxiety/fear and cause tremendous amounts of pain.
Common compulsive behaviors (ocd compulsions) used to alleviate obsessions may include the following.
- Avoiding your cat
- Asking reassurance from loved ones (if you did something to your cat)
- Hiding sharp utensils such as knives and razors (just in case)
- Not spending as much time with your cat as you once did
These obsessions are considered “common” in regards to OCD. This is how OCD comes after the things that we love and cherish the most.
Related Article(s) – Planning Care For A Patient With OCD
The Impact Of OCD On Quality of Life
Since OCD is a chronic disorder and general symptoms will likely be present for most of your life, one might anticipate a drop in overall quality of life. Furthermore, the sheer nature of the disease (obsessions and compulsions) also impacts everyday quality of life in patients.
Simple everyday tasks such as taking out the trash and/or going to the bathroom might feel impossible to accomplish in the perspective of a sufferer of the disease. Moreover, these “simple” tasks will generate an abnormal amount of stress and anxiety throughout the day, leaving individuals feeling lethargic and unmotivated.
According to The Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, Obsession severity was found to significantly predict patient quality of life. Moreover, Comorbid depression severity was the single greatest predictor of poor quality of life, affecting roughly 54% patients.
Can You Live With OCD Without Treatment?
Can you live with OCD without treatment? Yes. Will life become enjoyable if OCD is left untreated? Hell no.
Leaving OCD unattended is really not recommended, as you will most likely experience worse and more severe symptoms in the process. Moreover, as you begin to delay treatment your journey to control and “cope” the disease becomes exponentially difficult.
According to The European Psychiatry, “ longer duration of untreated illness in OCD is associated with poorer outcome in terms of response to SRI treatments”. In addition, overall quality of life will be affected the most if OCD is left untreated.
Furthermore, an individual with OCD who refuses appropriate treatment risks developing other comorbid disorders such as depression (40.7%), anxiety disorders(75.8%) and mood disorders (63.3). Other common comorbid OCD disorders may include tic disorders, ADHD and various eating disorders.

Moreover, according to Dr Umberto Albert’s book (Suicide Risk in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder and Exploration of Risk Factors: A Systematic Review) lifetime suicide attempts in OCD sufferer(s) is at 14%, greater than earlier anticipated.
In addition, untreated OCD may lead to developing substance abuse in patients. Due to the nature of the disease and the stress it generates, it’s normal to develop an appetite for drug and alcohol use in order to ease symptom severity and anxiety levels.
However, these actions are detrimental to OCD and will likely increase/worsen symptoms making the disease severe. Furthermore, According to The Journal Of Anxiety Disorders, 27% of OCD patients suffer from substance abuse. Interestingly, 70% reported that the onset of OCD preceded their substance abuse by at least 1 year.
Related Article(s) – Is OCD Treatable Without Medication?
Can OCD Cause Death?
Unfortunately, there are reasons to believe that OCD may cause death. According to a 2016 study, “The presence of OCD was associated with a significantly increased mortality risk. Comorbid anxiety disorders, depression, or substance use disorders further increased the risk”.
Moreover, other unnatural causes of death in regards to OCD patients include the following
- Autoimmune diseases
- Cancer
- Circulatory system diseases
- Respiratory diseases and allergies
- Gastrointestinal diseases
- Neurological disorders
- Sleep problems
- Chronic pain
- Suicide attempts
When Should You Seek Effective Treatment for OCD?
When OCD begins to interfere with everyday life, increasing stress and anxiety throughout the day, you should seek treatment. Moreover, as symptoms begin to increase in both frequency and severity resulting in wasted hours and energy, immediate action should be taken in seeking treatment.
In addition, it is important to know that the earlier you start treatment in your OCD journey, the more brief and easy it becomes later on in the process. However, delaying treatment will have the exact opposite effect as OCD will become much more difficult to treat and control.
Treatment Methods Used For OCD
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder is a mental health condition characterized by the presence of obsessions (persistent and intrusive thoughts, images, or urges) and compulsions (repetitive behaviors or mental acts performed to alleviate distress or prevent a feared outcome). Effective Treatment typically involves a combination of psychotherapy, medication, and self-help strategies.
Here’s an explanation of the commonly used approaches to treat OCD:
Cognitive-Behavior Therapy (CBT):
CBT is the most effective psychotherapy approach for OCD. It involves two main components: exposure and response prevention (ERP) and cognitive restructuring.
Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP)
ERP is the cornerstone of OCD treatment. It involves intentionally exposing the individual to situations, thoughts, or images that trigger their obsessions, without engaging in the associated compulsive behaviors. The gradual and systematic exposure helps individuals learn to tolerate anxiety and break the cycle of obsessions and compulsions.
Cognitive Restructuring
This component focuses on identifying and challenging the irrational beliefs and thought patterns that contribute to OCD. By examining and modifying distorted thinking patterns, individuals can develop more realistic and adaptive ways of interpreting their obsessions.
Medication
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are the most commonly prescribed medications for OCD. These antidepressant medications, such as fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, and sertraline, help regulate serotonin levels in the brain, which can reduce the symptoms of OCD. It’s important to note that medication should be prescribed and monitored by a qualified healthcare professional, and it may take several weeks to see the full effects.
Self-Help Strategies
In addition to therapy and medication, individuals with OCD can benefit from self-help strategies to manage their symptoms and improve their well-being. These strategies may include:
Psychoeducation
Learning about OCD, its symptoms, causes, and treatment approaches can empower individuals and help them understand that they are not alone.
Stress Management
Implementing stress-reducing techniques like deep breathing, mindfulness meditation, and relaxation exercises can help individuals cope with anxiety and reduce the frequency and intensity of OCD symptoms.
Healthy Lifestyle
Engaging in regular physical exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, getting sufficient sleep, and avoiding substances like drugs and alcohol can support overall mental health and reduce OCD symptoms.
Support System
Building a strong support network of family, friends, or support groups can provide emotional support, understanding, and encouragement during the treatment process.
It’s important to consult with a mental health professional, such as a psychologist or psychiatrist, who specializes in OCD treatment. They can conduct a comprehensive assessment, provide an accurate diagnosis, and develop an individualized treatment plan based on the severity of symptoms and the individual’s specific needs.
Thoughts on What Will Happen if OCD is Left Untreated
All in all, leaving OCD unattended and untreated is never a recommended approach. As we observed and analyzed various studies, untreated OCD is a risky game to play. Moreover, delaying treatment is also detrimental to the recovery process as it becomes more difficult to treat the disease later on.
This post was all about What Will Happen if OCD is Left Untreated?




